Colorimetric detection of creatinine using its specific binding peptides and gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
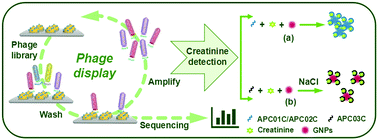
Creatinine in serum and urine is an established biochemical marker for monitoring chronic kidney disease. Moreover, peptides possess unique attributes, such as a low molecular weight and the ease of synthesis and modification, which render them suitable for the recognition of creatinine. In this study, we obtained three kinds of peptides with specific affinities to creatinine by using the phage display technology. Further, a new method was developed for the selective detection of creatinine by combining gold nanoparticles (GNPs) and peptide probes; consequently, a creatinine complex was formed. This novel assay is based on the distance-dependent optical properties of GNPs. Due to the aggregation or dissociation of GNPs, the concentration of creatinine can be detected by visually monitoring the purple-red changes or using a UV-visible spectrometer. The proposed method was successfully employed for analyzing the creatinine content in human urine. The unique synergistic coordination between GNPs and peptides improves the selectivity and specificity for the creatinine detection. Furthermore, we believe that the proposed method can be utilized for the colorimetric detection of other biomolecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...