A new chloro-substituted dicyanoisophorone-based near-infrared fluorophore with a larger Stokes shift and its application for detecting cysteine in cells and in vivo†
Abstract
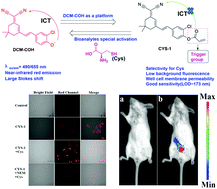
Many dicyanoisophorone-based fluorophores with an optical hydroxyl group have been explored to meet different imaging needs along with the rapid and wide development of molecular fluorescence bioimaging in recent years. However, most of them used to need the addition of slight alkaline conditions to dissociate a proton for near-infrared emission and this limits their wider application in complex bio-systems. Aiming to modify the dicyanoisophorone-based fluorophore platform with an optically tunable hydroxyl group for better biocompatibility for molecular bioimaging in vivo, we developed a new chloro-substituted dicyanoisophorone-based near-infrared fluorophore (DCM-COH) which featured simple preparation (two steps), good optical properties and showed potential application prospects. As a proof-of-concept, DCM-COH was applied to design a new probe (CYS-1) for detecting cysteine. CYS-1 (λex/em = 490/655 nm) possessed a large Stokes shift (165 nm), low toxicity, good sensitivity (detection limit of ∼173 nM) and selectivity for rapid cysteine detection. More importantly, CYS-1 successfully served as an indicator for imaging cysteine in cells and in vivo. Fluorophore DCM-COH may act as a potential platform to be extended as a capable tracking tool in biological chemistry and preclinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...