Removal of paraquat from aqueous solutions by a bentonite modified zero-valent iron adsorbent†
Abstract
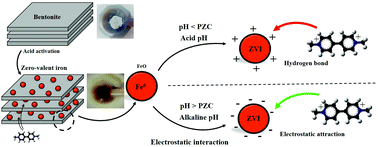
In the present study, a bentonite-supported zero-valent iron (B-ZVI) composite is synthesized from bentonite, which was then used as an adsorbent to remove paraquat contamination from water. The as-prepared B-ZVI composite was characterized by FE-SEM, EDS, XRD and element mapping. Various factors such as the pH, initial concentration of paraquat and mass of adsorbent influenced the removal of paraquat in batch experiments based on CCD. The equilibrium data were better explained by the Langmuir isotherm model and subsequently the adsorption capacity (qm) based on the Langmuir model was 6.784 mg g−1. Thermodynamic evaluation illustrated that the adsorption of paraquat by B-ZVI was spontaneous in nature and an endothermic process. The effect of different salts including NaCl, Na2CO3, Na2SO3 and KNO3 on the adsorption of paraquat was studied. It has been found that the presence of NaCl, Na2SO3, Na2CO3 and KNO3 salt (0.1 M) in solution has a considerable effect on the adsorption behavior.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...