Highly sensitive electrode materials for the voltammetric determination of nitrofurantoin based on zinc cobaltate nanosheets
Abstract
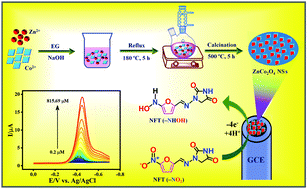
Transition metal-doped metal oxides with a typical spinal structure are considered to be the most promising electrodes for superior electrochemical sensors because of their better electrochemical conductivity and electron transfer properties than those of individual metal oxides. Here, we demonstrated the simple preparation of spinel-type zinc cobaltate nanosheets through the polyol method for the electrochemical determination of nitrofurantoin. Various spectroscopic techniques were used to characterize the as-synthesized material, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and differential pulse voltammetry techniques were used to study the electrochemical properties. The electrochemical detection of nitrofurantoin was performed based on the fabricated electrode, generating outstanding electrocatalytic performance with a limit of detection of 0.013 μM and excellent sensitivity of 2.866 μA μM−1. Moreover, the modified electrode exhibits excellent selectivity and good recoveries in real sample analysis towards the detection of nitrofurantoin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...