Chiral separation of five antihistamine drug enantiomers and enantioselective pharmacokinetic study of carbinoxamine in rat plasma by HPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
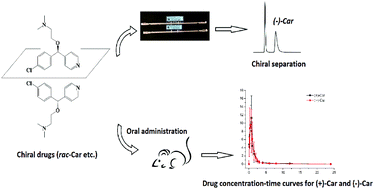
The chiral separation of five antihistamine drugs including meclizine, cloperastine, azelastine, carbinoxamine and mequitazine was studied by HPLC combined with chiral stationary phases. The effect of chiral columns, the types and contents of organic modifiers, and the concentrations of basic additive on the chiral separation was evaluated and optimized in detail. The best enantioselectivity for these compounds was observed using Chiralpak IA and Chiralpak ID as chiral columns. In particular, baseline separation of carbinoxamine with the largest resolution of 3.82 was achieved using a Chiralpak ID column with the mobile phase of acetonitrile–water–ammonia solution (90 : 10 : 0.1, v/v/v). Based on this result, an enantioselective HPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for determination of carbinoxamine enantiomers in rat plasma. Also, this method was successfully applied in evaluating the pharmacokinetic profiles of carbinoxamine enantiomers. Good linearity (r > 0.99) for both enantiomers over a concentration range of 0.1–100 ng mL−1 was obtained. The accuracy ranged from 87.4% to 113.8%, and the intra-day and inter-day precisions were below 9.4% for (+)- and (−)-carbinoxamine at three quality control levels. The pharmacokinetic parameters demonstrated that the absorption and elimination processes of carbinoxamine enantiomers were not stereoselective, and chiral inversion did not occur either in rats.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...