Electrostatic grafting of graphene onto polyamide 6,6 yarns for use as conductive elements in smart textile applications
Abstract
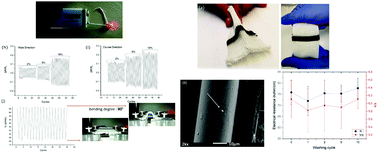
Electrostatic graphene-grafted conductive yarns were prepared based on a scalable manufacturing method using conventional polyamide 6,6 (PA 6,6) multifilament yarns, common in the textile industry. Graphene oxide (GO) shows negative surface charge at any pH and PA 6,6 has an isoelectric point (IEP = pH|ζ=0) of 3.6. When GO and a polymer have the same charge sign, the resulting electrostatic interaction is repulsive and an electrostatic attraction does not arise until the polymer backbone has an oppositely charged sign compared to the GO nanosheets. To achieve this, yarns were modified with protonated chitosan (CS) followed by dip-coating with GO, resulting in electrostatic grafting of oxygen functional groups of GO onto amino groups of CS polymer chains. This coating process provides durable electrically conductive yarns (3 × 10−2 to 4 × 10−2 S m−1) with an excellent fastness to washing. It leads to the realization of graphene-grafted yarns as building elements of smart textiles, obtaining metal-free textile sensors. These yarns are capable of supplying power to an LED light using a 9 V battery and are expected to be an excellent candidate for feeding V-bed flat-knitting, Jacquard and raschel knitting machines. To achieve this, a wearable tactile sensor was designed and prepared using a flat-knitting machine and the sensor was characterized through electrical, mechanical, and electromechanical measurements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...