Application of magnesium ion doped carbon dots obtained via hydrothermal synthesis for arginine detection†
Abstract
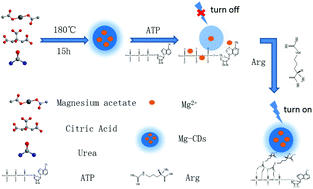
As a new-type of nanomaterial, carbon dots (CDs) have been extensively applied in biochemistry-related fields. In this study, a single-step hydrothermal method was used to rapidly and conveniently synthesize Mg-doped CDs (Mg-CDs) with stable fluorescence, and favorable water solubility and dispersity, with the quantum yield reaching 26.86%. With adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as a switch, a fluorescent sensor was developed to monitor arginine based on the Mg-CDs. The surface of the Mg-CDs had many organic functional groups, and ATP could bind effectively to these groups, thereby quenching the fluorescence of the Mg-CDs. In addition, the electrostatic interaction between arginine and ATP displayed covalent stability, which enhanced the fluorescence of the Mg-CDs. After constructing the probe sensor, we also systematically optimized the experimental conditions and investigated parameters such as pH and ATP concentration. Under the optimum test conditions, the constructed fluorescence test sensor revealed a linear relationship with arginine within the range of 0.3–130 μmol L−1, with a low detection limit of 0.15 μmol L−1. The sensor exhibited high specificity, excellent stability and good reproducibility. The results showed the satisfactory determination of arginine in human urine with a recovery of 97.0–100%. The relative standard deviation value was less than 4.1%. The present study can be used as a highly selective and sensitive colorimetric method for the quantification of arginine from various aqueous media.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...