The first examples of triply bonded dirhenium(II,II) complexes that contain bis(diphenylphosphino)methane and dithiocarbamato ligands: spectroscopic, structural, cytotoxicity and computational studies†
Abstract
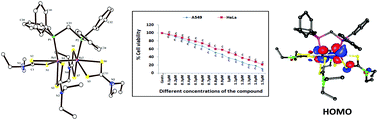
Sodium salts of dimethyldithiocarbamate, diethyldithiocarbamate and pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate react with the triply bonded dirhenium (II,II) complex Re2(μ-Ph2PCH2PPh2)2Cl4 (1) in refluxing ethanol to afford the products of the type Re2(μ-Ph2PCH2PPh2)(LR)4 (2(LR)) where LR represents the dithiocarbamato ligands [LR = S2CNMe2, 2(LMe); S2CNEt2, 2(LEt) and S2CN(CH2)4, 2(LPyr)]. These are the first examples of dithiocarbamato chelated dirhenium complexes with a Re24+ core containing Ph2PCH2PPh2 (dppm) ligand. The spectral (IR, UV-vis, NMR, ESI-MS) and electrochemical properties of the complexes are reported. The identity of 2(LEt) has been established by single-crystal X-ray structure determination (Re–Re distance 2.3196(8) Å). The electronic structure and the absorption spectra of the complexes are scrutinized by density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) analyses. DFT analysis shows that the highest occupied molecular orbitals are mainly metal δ* based orbitals. The complex 2(LEt) was also screened in vitro for its antiproliferative properties against human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells (A549), the cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by MTT assay which indicates its preferential cytotoxicity against the cancer cells (A549, HeLa).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...