Excellent adsorption–photocatalysis synergistic activity of 3D–3D flower-like BiOBr/graphene hydrogel composite and the removal of potassium butyl xanthate†
Abstract
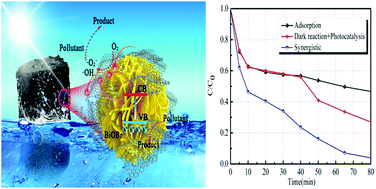
A 3D–3D flower-like bismuth bromide (BiOBr)/graphene hydrogel (BiOBr/GH) composite was synthesized via a two-step hydrothermal method. The scanning electron microscopy results confirmed that the three-dimensional (3D) flower-like BiOBr microspheres can be successfully loaded onto three-dimensional graphene oxide (GO) to form BiOBr/GH composites via the hydrothermal method. The photocatalytic and adsorptive properties of BiOBr/GH on potassium butyl xanthate (PBX) were systematically investigated. Results showed that 80%-BiOBr/GH possessed higher photocatalytic efficiency than other composites and BiOBr, and its PBX removal efficiency was 1.83 times higher than that of BiOBr under irradiation using a 300 W xenon lamp. The composites had excellent adsorption properties, which increased with the introduction of GH. The adsorption performance of 75%-BiOBr/GH was better than that of the other composites. PBX could be almost completely removed after 85 minutes via the synergistic effect of photocatalytic degradation and adsorption. Furthermore, the PBX removal efficiency after six cycles still reached over 70%. The 3D structure not only facilitated the migration and separation of photogenerated carriers, but also made the materials easy to recycle. This property is conducive to the treatment of pollutants in the environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...