Preparation and characterization of an Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite with enhanced photocatalytic performance toward rhodamine B
Abstract
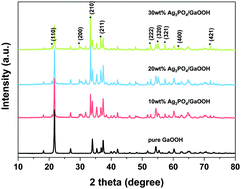
A highly efficient Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite was innovatively prepared and its photocatalytic performance was evaluated through degrading rhodamine B (RhB) under illumination, in this paper. Characterizations including XRD, SEM-EDS, TEM, FT-IR, XPS, UV-Vis DRS, PL and EPR were performed to analyze the properties of the Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite. The SEM-EDS results indicated that Ag3PO4 particles were dispersed on the surface of GaOOH sticks. The (210) plane of Ag3PO4 particles and the (200) plane of GaOOH sticks were simultaneously observed in the TEM results. UV-Vis DRS analysis indicated that the spectrum of the Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite showed a significant red shift compared to that of pure GaOOH. PL spectra also indicated that the construction of the Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite significantly declined the recombination rate of photogenerated electrons-hole pairs. The photocatalytic degradation experiments showed that the 30 wt% Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite demonstrated excellent performance under illumination. After a reaction time of 60 min, the decolorization rate of RhB was up to 97.83% using the 30 wt% Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite. Further studies confirmed that the 30 wt% Ag3PO4/GaOOH composite had good stability and the contribution of active species during degradation was of the order h+ > ˙O2− > ˙OH. The results of this study would provide a new perspective for improving the applications of wide band gap semiconductors, particularly for light-induced degradation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...