A bis(thiosemicarbazonato)-copper complex, a new catalyst for electro- and photo-reduction of CO2 to methanol†
Abstract
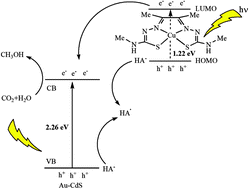
Diacetyl-2-(4-N-methyl-3-thiosemicarbazone)-3-(4-N-amino-3-thiosemicarbazone) (H2ATSM) reacts with CuCl2 to form a copper complex, Cu-ATSM, a new catalyst for electrochemically and photochemically driven CO2 reduction to methanol. As an electrocatalyst, this copper complex can catalyse methanol generation from a CO2-saturated buffer with a turnover frequency (TOF) of 2844 moles of methanol per mole of catalyst per hour and a faradaic efficiency of 74% during a 6 h electrolysis. Under blue light (λ = 469 nm), combining with Au–CdS nanoclusters (Au–CdS NCs) as a photosensitizer, and ascorbic acid (H2A) as a sacrificial electron donor, this copper complex can catalyse methanol generation with a turnover number (TON) of 4067 moles of methanol per mole of catalyst (mol of cat−1) and a methanol selectivity of 74%. The highest apparent quantum yield (AQY) is 9.0%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...