High photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2–BiOBr composites via an in situ synthesis approach
Abstract
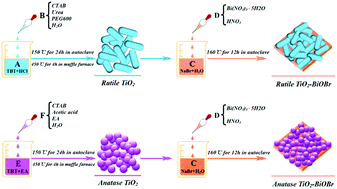
It is well known that rutile TiO2 has extremely inferior photocatalytic performance due to lower electron mobility and specific surface area than anatase TiO2. In addition, the photocatalytic performance of BiOBr is also not satisfactory due to small specific surface area and positive conduction band position. However, when the two above-mentioned catalysts were combined to form composites via an in situ synthesis approach, resulting that rutile TiO2–BiOBr composites exhibited a superior performance of almost the same photocatalytic effect as anatase TiO2–BiOBr composites, of which the apparent rate constant of MO photodegradation was approximately 1.6 times larger than that of anatase TiO2 and 6.3 times larger than that of BiOBr. To further investigate the reasons, the samples were characterized by XRD, TEM, DRS, EIS, BET, PL, etc. Although RT + BOB has better EIS or PL data than AT + BOB, the specific surface area of AT + BOB is larger than that of RT + BOB. In addition, it can be deduced that photogenerated holes are the dominant active species of TiO2–BiOBr composites by active species trapping experiments. Finally, a possible mechanism for the enhancement of photocatalytic performance of rutile TiO2–BiOBr composites was proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...