12-Hydroxy stearic acid appended new amphiphilic scaffolds for selective capture of hydrogen halides through supramolecular hydrogelation†
Abstract
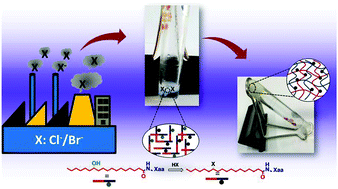
12-Hydroxystearic acid (12-HSA) appended new amphiphilic scaffolds reveal excellent hydrogelation propensity in the presence of aqueous acids and vapors of HCl/HBr. This selective entrapment efficiency towards hydrogen halides demonstrates an unprecedented route for the successful removal of toxic chemicals, thus providing a safe and easy protocol for environment management. We anticipate that the halide derivative of the amphiphile plays a vital role in driving the self-assembly mechanism and eventually the hydrogelation phenomena.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...