Synthesis of ribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleosides under plausible prebiotic conditions within self-assembled supramolecular structures†
Abstract
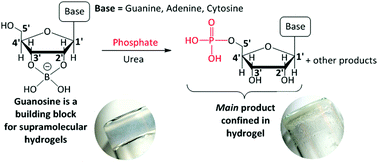
Abiotic synthesis of ribonucleotides, mainly at the 5′ position, from the corresponding ribonucleosides within self-assembled supramolecular structures, based on guanosine:borate hydrogels, was carried out in the temperature range of 70–90 °C, using urea and a phosphate source (K2HPO4 or hydroxyapatite). Phosphorylation is possible at initial concentrations of guanosine lower than 20 mM and it is more efficient using wet/dry cycles. Monoamidophosphate (and, eventually, diamidophosphate), diamidodiphosphate and pyrophosphate are intermediates in the synthesis of ribonucleotides. These conclusions are supported by NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry analysis of samples. On the other hand, after reaction, hydrogels can produce globular aggregates by the addition of water and decreasing temperature, thus confirming that ribonucleotides, once activated under suitable conditions, could form polyribonucleotides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...