A new voltammetric immunosensing platform for prostate-specific antigen based on the Cu(ii)-pyrophosphate ion chelation reaction†
Abstract
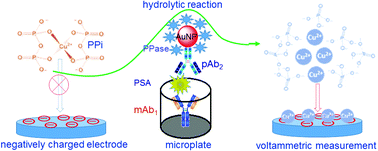
A new electrochemical immunoassay was designed for the sensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) via a pyrophosphatase (PPase)-hydrolysed Cu(II)-coordinated pyrophosphate ion (Cu2+-PPi) complex, accompanying the release of Cu(II) ions and capture on a negatively charged electrode. This system involved a sandwiched immunoreaction with nanogold-labeled PPase/detection antibodies on a polystyrene microplate, enzymatic hydrolysis, Cu(II) release and voltammetric measurement. The voltammetric signal is derived from the as-released Cu(II) ions within the applied potential on the electrode. Under optimum conditions, our strategy exhibited a good voltammetric response for the analyte, and allowed determination of PSA at a concentration as low as 5.2 pg mL−1. Good precision, high specificity and acceptable accuracy were achieved for the detection of PSA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...