Mo or W catalysts promoted with Ni or Co supported on modified bentonite for decane hydroconversion
Abstract
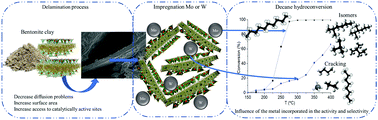
A clay mineral-type modified bentonite, produced via delamination and subsequent incorporation of AlZr and AlCe species to modulate their acid properties, was used to obtain bifunctional catalysts with the incorporation of NiMo, CoMo, NiW and CoW. The catalysts were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR) and diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier-transform spectra with a probe molecule (NH3-DRIFTS). The catalytic performance was evaluated in the hydroconversion of decane. The main differences in catalytic performance were attributed to the reductive and acid properties of the catalysts. Indeed, when Mo was used, there was a higher conversion compared to W catalysts, which correlated with the greater number of reducible species at lower temperatures. Solids with a promoter/metal ratio of 0.4 presented the best catalytic performance, which is attributed to the fact that this ratio improves the formation of NiW, NiMo, CoW and CoMo species on the surface of solids. On the other hand, the catalysts obtained from the mineral modified with AlCe showed better catalytic activity compared to catalysts containing AlZr as an acidity enhancer. The different processes and elements used give us information to carry out controlled processes for the generation of acid sites that respond to a specific orientation of the decane hydroconversion reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...