A new fluorescence probe comprising nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for the selective and quantitative determination of cerium(iv)†
Abstract
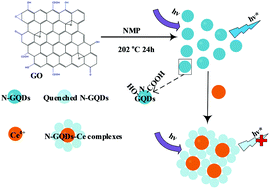
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have been widely applied in the fields of photocatalysis, bioimaging, drug delivery, metal ion detection and up-conversion photoluminescence, etc. This work introduces N-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs), prepared via a one-step green wet chemical method using graphene oxide (GO) as a raw material, followed by dialysis, to create a new fluorescence sensor for rare earth elements (REEs). The obtained N-GQDs with rich oxygen functional groups showed a strong blue emission which was almost unaffected by extreme pH conditions. Due to the selective coordination to Ce4+ over other REEs, the N-GQDs can be used as a sensitive and selective chemo-sensor of Ce4+ ions in aqueous solution. The concentration range and the detection limit of the N-GQDs fluorescence probe were 1–44 μM and 0.8352 μM for Ce4+, respectively. The possible quenching mechanism was also explored via material characterization tools, such as FTIR, XPS, UV-vis and DLS analysis. The interference from other REEs was negligible during the quantitative determination of Ce4+. This method proved to be simple, sensitive, low cost, and also reliable for practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...