Cu(ii), Ir(i) and CuO nanocatalyzed mild synthesis of luminescent symmetrical and unsymmetrical bis(triazolylmethyl)quinoxalines: biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, live cell imaging and biomolecular interaction†
Abstract
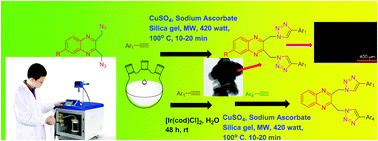
Quinoxaline derivatives play versatile roles in various fields of science. Thus different types of scaffolds have been designed with these quinoxaline moieties to make them more efficient for preparation of various biologically active materials in the pharmaceutical industry. The ability of quinoxaline moieties has been reinforced by introducing triazole rings into them with the aid of a “click reaction” following environmentally friendly green techniques in the presence of a Cu(II) catalyst as well as in the presence of a CuO nanomaterial under microwave irradiation. The novelty of our work is being highly focussed on the introduction of unsymmetrical triazole rings with the isolation of mono triazolyl quinoxaline derivatives using an Ir(I) catalyst in aqueous medium and on the capability of the CuO nanomaterial in catalyzing a “click reaction” in various biological media. The role of our synthsized bis(trizolylmethyl)quinoxaline compounds as cytotoxic agents has been confirmed with clear evidence from a DNA and BSA binding study, stability study, viscosity study and MTT assay. Due to the detecting ability of live cancer cells, high cellular uptake, biocompatibility and high cytoselectivity of these scaffolds, ultimately compound 6g has been established as a cancer theranostic drug.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...