Acceleration of ammonium phosphate hydrolysis using TiO2 microspheres as a catalyst for hydrogen production†
Abstract
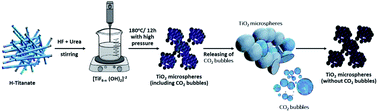
Titania microspheres are considered an adequate material with low cost and easily attainable pathways, and can be utilized in photocatalytic H2 production to solve the energy crisis. Spherical porous titanium dioxide materials, with nanostructure composition, were chemically synthesized from titanate nanotubes via a simple hydrothermal technique, then added as a catalyst to accelerate the route of ammonium phosphate hydrolysis for hydrogen production. The mechanism of sphere formation from titanate nanotubes is elucidated in detail through the current study. The prepared materials were applied as a photocatalyst to facilitate the separation and transfer of photoinduced electrons, while preventing the recombination of electron–hole pairs. Experimental results show that the obtained microspheres possess significantly enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen (H2) production performance. The amount of photocatalytic hydrogen product using the microspheres is found to be ∼2.5 fold greater than that of titanate nanotubes. Analytical techniques such as field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), simulated visible solar light and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used for the evaluation and characterization of the developed products, as well as the elucidation of the route of hydrolysis in the hydrogen production process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...