Femtosecond laser-induced non-thermal welding for a single Cu nanowire glucose sensor†
Abstract
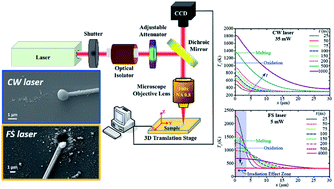
Copper nanowires (CuNWs) are a key building block to facilitate carrier conduction across a broad range of nanodevices. For integration into nanoscale devices, manipulation and welding of these nanowires need to be overcome. Based on high energy density laser processing investigation, we report on innovative welding of single CuNWs to a silver film using a tightly focused laser beam combined with manipulation of CuNWs through the dielectrophoresis (DEP) method. Two types of lasers, femtosecond (FS) and continuous-wave (CW), were employed to analyze, improve, and control Cu-NW melting characteristics under high energy density irradiation. The FS laser welding of CuNWs resulted in a metallic joint with a low contact resistance suitable for functional electronic nanodevices. Computational simulations using the 1-D heat diffusion equation and finite difference method (FDM) were performed to gain an insight into metal–laser interactions for high performance welded contact development. Simulation studies on lasers established contrasting melting behavior of metal under laser irradiation. The device feasibility of CuNW based welded contacts was evaluated in terms of the electrical performance of a glucose sensor. It was possible to sense glucose concentration down to 10−6 M, demonstrating a path towards integration of CuNWs into wearable, flexible nanoelectronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...