γ-Alumina-supported Pt17 cluster: controlled loading, geometrical structure, and size-specific catalytic activity for carbon monoxide and propylene oxidation†
Abstract
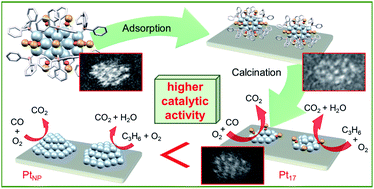
Although Pt is extensively used as a catalyst to purify automotive exhaust gas, it is desirable to reduce Pt consumption through size reduction because Pt is a rare element and an expensive noble metal. In this study, we successfully loaded a Pt17 cluster on γ-alumina (γ-Al2O3) (Pt17/γ-Al2O3) using [Pt17(CO)12(PPh3)8]Cln (n = 1, 2) as a precursor. In addition, we demonstrated that Pt is not present in the form of an oxide in Pt17/γ-Al2O3 but instead has a framework structure as a metal cluster. Moreover, we revealed that Pt17/γ-Al2O3 exhibits higher catalytic activity for carbon monoxide and propylene oxidation than γ-Al2O3-supported larger Pt nanoparticles (PtNP/γ-Al2O3) prepared using the conventional impregnation method. Recently, our group discovered a simple method for synthesizing the precursor [Pt17(CO)12(PPh3)8]Cln. Furthermore, Pt17 is a Pt cluster within the size range associated with high catalytic activity. By combining our established synthesis and loading methods, other groups can conduct further research on Pt17/γ-Al2O3 to explore its catalytic activities in greater depth.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...