A copper complex formed with neurokinin B: binding stoichiometry, redox properties, self-assembly and cytotoxicity†
Abstract
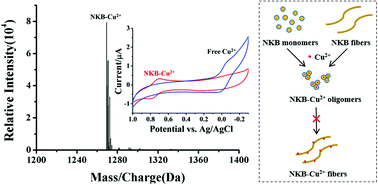
The tachykinin neuropeptide of neurokinin B (NKB) is a copper-binding amyloid peptide with important roles in the regulation of physiological functions and pathophysiological processes in the central and peripheral nervous systems. In this work, the formation of a NKB–Cu2+ complex in a 1 : 1 stoichiometry was confirmed by mass spectrometry. The self-assembly of NKB and its mutant species was investigated by Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence assay and atomic force microscopy (AFM), and at the same time, the effect of Cu2+ on the aggregation of NKB was studied. As evidenced by cyclic voltammetry, the redox potential of NKB–Cu2+ was determined to be 0.77 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). It has been demonstrated that NKB at low concentrations exerts its neuroprotective function by inhibiting Cu2+-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA). In comparison with equivalent Cu2+, the peptide–Cu2+ aggregates aggravated the viability of PC-12 cells more seriously in the absence of AA. These results should be extremely valuable for understanding the NKB/Cu2+ interactions and the toxicity mechanism of Cu2+ associated with neurodegenerative diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...