Lipid extraction from dried blood spots and dried milk spots for untargeted high throughput lipidomics†
Abstract
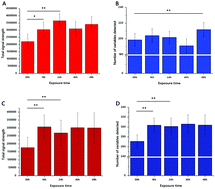
Dried blood spots (DBS) and dried milk spots (DMS) represent convenient matrices for collecting and storing human samples. However, the use of these sample types for researching lipid metabolism remains relatively poorly explored, and especially unclear is the efficiency of lipid extraction in the context of high throughput, untargeted lipidomics. A visual inspection of punched DBSs after standard extraction suggests that the samples remain largely intact. DMSs comprise a dense aggregate of milk fat globules on one side of the card, suggesting that part of the lipid fraction may be physically inaccessible. This led us to the hypothesis that decoagulating may facilitate lipid extraction from both DBSs and DMSs. We tested this hypothesis using a mixture of strong chaeotropes (guanidine and thiourea) in both DBS and DMS in the context of high throughput lipidomics (96/384w plate). Extraction of lipids from DMSs was tested with established extractions and one novel solvent mixture in a high throughput format. We found that exposure of DBSs to chaeotropes facilitated collection of the lipid fraction but was ineffective for DMSs. The lipid fraction of DMSs was best isolated without water, using a mixture of xylene/methanol/isopropanol (1 : 2 : 4). We conclude that decoagulation is essential for efficient extraction of lipids from DBSs and that a non-aqueous procedure using a spectrum of solvents is the best procedure for extracting lipids from DMSs. These methods represent convenient steps that are compatible with the sample structure and type, and with high throughput lipidomics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...