Investigation of thiazolyl–benzothiophenamides as potential agents for African sleeping sickness†
Abstract
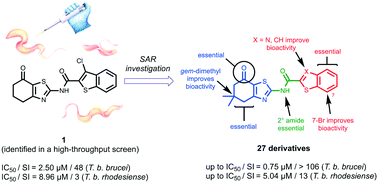
African sleeping sickness is a potentially fatal neglected disease affecting sub-Saharan Africa. High-throughput screening identified the thiazolyl–benzothiophenamide 1 to be active against the causative parasite, Trypanosoma brucei. This work establishes structure–activity relationships of 1, guiding the design of second generation derivatives. After screening against the clinically relevant species T. b. rhodesiense, the derivative 16 was identified as a suitable candidate for further investigation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...