Synthesis and evaluation of anticancer activity of new 9-acridinyl amino acid derivatives†
Abstract
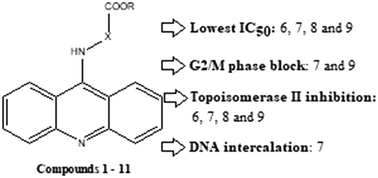
A series of eleven 9-acridinyl amino acid derivatives were synthesized using a two-step procedure. Cytotoxicity was tested on the K562 and A549 cancer cell lines and normal diploid cell line MRC5 using the MTT assay. Compounds 6, 7, 8 and 9 were the most active, with IC50 values comparable to or lower than that of chemotherapeutic agent amsacrine. 8 and 9 were especially effective in the A549 cell line (IC50 ≈ 6 μM), which is of special interest since amsacrine is not sufficiently active in lung cancer patients. Cell cycle analysis revealed that 7 and 9 caused G2/M block, amsacrine caused arrest in the S phase, while 6 and 8 induced apoptotic cell death independently of the cell cycle regulation. In comparison to amsacrine, 6, 7, 8, and 9 showed similar inhibitory potential towards topoisomerase II, whereas only 7 showed DNA intercalation properties. In contrast to amsacrine, 6, 7, 8 and 9 showed a lack of toxicity towards unstimulated normal human leucocytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...