Detection and beyond: challenges and advances in aptamer-based biosensors
Abstract
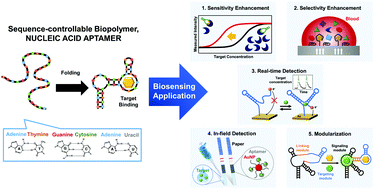
Beyond traditional needs of biosensors such as high sensitivity and selectivity for analyte detection, newly emerging requirements including a real-time detection ability and in-field applicability have been gradually emphasized to address clinical and environmental availability. Highly programmable, synthetic aptamers that can specifically recognize a broad range of targets have the potential to fulfill these requirements; cooperative binding to target molecules achieves a significant increase in sensitivity, and binding-induced structure-switching enables target detection even in complex mixtures. Due to the availability of chemical synthesis and functional modifications, these artificial ligand materials are easily installed in many devices, and the amenability to modularization allows the aptamer-based biosensors to diversify detectable targets and signaling processes. In this review, we highlight current progress in the development of aptamer-based, next-generation biosensors including new types of field-effect transistors, electrochemical detectors, and microfluidic devices. As the nucleic acid aptamers have been rapidly generated by various in vitro selection techniques, the use of the versatile nanostructures is expected to expand further to include in-field and real-time biosensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...