Binary treatment of PEDOT:PSS films with nitric acid and imidazolium-based ionic liquids to improve the thermoelectric properties†
Abstract
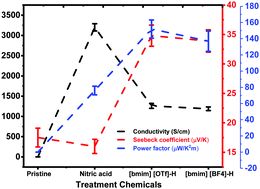
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) is one of most prominent organic conductive polymer-based thermoelectric (TE) materials. Numerous combinations of doping and dedoping processes have been demonstrated to optimize the doping level of PEDOT:PSS films, and subsequently enhance electrical conductivity (σ) and Seebeck coefficient (S) of PEDOT:PSS films. This work established that binary post-treatment with nitric acid and imidazolium-based ionic liquids improved the σ and S. The σ of PEDOT:PSS film was significantly improved from 0.30 to 1260 ± 61 S cm−1 and its corresponding S was simultaneously increased from 16 ± 1.2 to 34.8 ± 1.8 μV K−1, giving rise to a power factor of 152 ± 11.2 μW m−1 K−2 at optimal conditions. The thermal conductivity (κ) concurrently declined from 0.6 to 0.3 W m−1 K−1 for the untreated and treated PEDOT:PSS films, correspondingly, achieving a figure of merit (ZT) value of ∼0.12 at 300 K. The TE performance enhancement of PEDOT:PSS films was largely attributable to the change in the doping level of PEDOT as evidenced by the overall increase in mobility and carrier concentration, and hence resulted in concurrent increase in the σ and S, which were corroborated by different characterization methods. Studies on long-term stability of PEDOT:PSS films at 70 °C and 75% RH for 20 days showed that more than 85% σ and S was retained, showing potential applications for this binary post-treatment method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...