Electrocatalytic properties of {Mo3S4}-based complexes with regard to the hydrogen evolution reaction and application to PEM water electrolysis†
Abstract
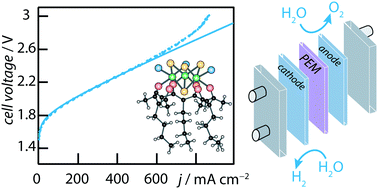
We report on the synthesis and the electrochemical characterization of two [Mo3S4]4+ nanoclusters, [Mo3S4(acacbut)3]Cl and [Mo3S4–Pd(acacbut)3]Cl. Their electrochemical properties have been measured in solution in organic and in aqueous media, by cyclic voltammetry, linear sweep potential voltammetry and chrono-coulometry at controlled potential. The different redox couples have been identified. Their electrochemical activity with regard to the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) has been determined by dropwise addition of controlled amounts of formic acid in acetonitrile. The turn over frequency of the two compounds has been determined to compare their HER activity. Then the two compounds have been functionalized onto two different carbonaceous substrates (graphene and carbon black) of practical interest for applications in water electrolysis cells. The polarization curves and Tafel plots have been measured in 0.1 M H2SO4 aqueous solutions. Finally, the two complexes have been implemented at the cathode of a PEM water electrolysis cell. The polarization curves have been measured and compared to those obtained with metallic platinum under similar operating conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...