Differential antimicrobial and cellular response of electrolytically metalized halloysite nanotubes having different amounts of surface metallization
Abstract
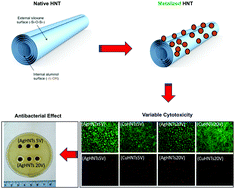
We demonstrate an electrolytic method to metalize the outer surface of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs). Different metal HNT (mHNT) combinations (copper, silver, zinc) were produced with metal content in the 5–30 wt% range. mHNTs were characterized using a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). Different amounts of surface/lumen metal content of a system can confer differing antimicrobial/cellular response; hence, it is essential to assess the antimicrobial/cellular response as a function of metal content. Cellular response after exposure to mHNTs was studied in Staphylococcus aureus and pre-osteoblasts, respectively. Coated mHNTs could easily be identified using the characterization methods, and contrasting bacterial and cellular responses were obtained, which we propose was due to the extent of metallization. These findings demonstrate the potential of this method for creating metal-coated HNTs and suggest they have potential as an implant coating solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...