Melamine adsorption on carbon materials: impact of carbon texture and surface chemistry†
Abstract
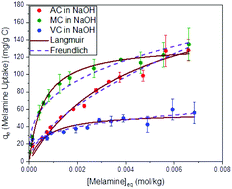
In this work, a comparative study between three carbon materials has been carried out to investigate the impact of the micro/mesoporous structure of the carbon substrate on their adsorption capabilities. The study included two commercial carbons: Darco KB-G (AC), and Vulcan XC-72R (VC). The third carbon material was a mesoporous material (MC), with tailored micro/mesoporous structure and surface area obtained by carbonization of a resorcinol–formaldehyde (RF) polymer gel using both soft and hard template materials. Melamine was used as a model adsorbate in both acid and alkaline solutions. For all carbons, melamine adsorption was found to be pH dependent with higher adsorption from alkaline solutions than from acidic solutions. To the best of our knowledge, these are the first reported values for the adsorption of melamine to these carbon materials. Adsorption data obtained using the Langmuir model were compared with theoretical studies involving melamine as a building block in the self-assembly of molecular structures on carbon substrates, and analyzed using the results of several characterization studies carried out as part of this research work, some of which include nitrogen and CO2 adsorption isotherms, Raman spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...