Remotely tunable microfluidic platform driven by nanomaterial-mediated on-demand photothermal pumping†
Abstract
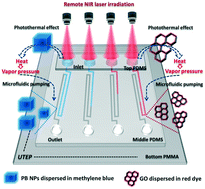
The requirement of on-demand microfluidic pumps and instrument-free readout methods remains a major challenge for the development of microfluidics. Herein, a new type of microfluidic platform, an on-demand photothermal microfluidic pumping platform, has been developed using an on-chip nanomaterial-mediated photothermal effect as novel and remotely tunable microfluidic driving force. The photothermal microfluidic pumping performance can be adjusted remotely by tuning the irradiation parameters, without changing on-chip parameters or replacing enzymes or other reagents. In contrast to graphene oxide, Prussian blue nanoparticles with higher photothermal conversion efficiency were used as the model photothermal agent to demonstrate the proof of concept. The on-chip pumping distance is linearly correlated with both the irradiation time and the nanomaterial concentration. The applications of photothermal microfluidic pumping have been demonstrated in multiplexed on-chip transport of substances, such as gold nanoparticles, and visual quantitative bar-chart detection of cancer biomarkers without using specialized instruments. Upon contact-free irradiation using a laser pointer, a strong on-chip nanomaterial-mediated photothermal effect can serve as a robust and remotely tunable microfluidic pump in a PMMA/PDMS hybrid bar-chart chip to drive ink bars in a visual quantitative readout fashion. This is the first report on a photothermal microfluidic pumping platform, which has great potential for various microfluidic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...