PRESCIENT: platform for the rapid evaluation of antibody success using integrated microfluidics enabled technology†
Abstract
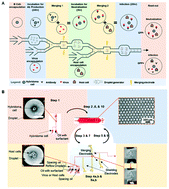
Identifying antibodies (Abs) that neutralize infectious agents is the first step for developing therapeutics, vaccines, and diagnostic tools for these infectious agents. However, current approaches for identifying neutralizing Abs (nAbs) typically rely on dilution-based assays that are costly, inefficient, and only survey a small subset of the entire repertoire. There are also intrinsic biases in many steps of conventional nAb identification processes. More importantly, conventional assays rely on simple Ab–antigen binding assays, which may not result in identifying the most potent nAbs, as the strongest binder may not be the most potent nAb. Droplet microfluidic systems have the capability to overcome such limitations by conducting complex multi-step assays with high reliability, resolution, and throughput in a pico-liter volume water-in-oil emulsion droplet format. Here, we describe the development of PRESCIENT (Platform for the Rapid Evaluation of antibody SucCess using Integrated microfluidics ENabled Technology), a droplet microfluidic system that can enable high-throughput single-cell resolution identification of nAb repertoires elicited in response to viral infection. We demonstrate PRESCIENT's ability to identify Abs that neutralize a model viral agent, Murine coronavirus (murine hepatitis virus), which causes high mortality rates in experimentally infected mice. In-droplet infection of host cells by the virus was first demonstrated, followed by demonstration of in-droplet neutralization by nAbs produced from a single Ab-producing hybridoma cell. Finally, fluorescence intensity analyses of two populations of hybridoma cell lines (nAb-producing and non-nAb-producing hybridoma cell lines) successfully discriminated between the two populations. The presented strategy and platform have the potential to identify and investigate neutralizing activities against a broad range of potential infectious agents for which nAbs have yet to be discovered, significantly advancing the nAb identification process as well as reinvigorating the field of Ab discovery, characterization, and development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...