Construction of 3D native elemental maps for large biological specimens using LA-ICP-MS coupled with X-ray tomography†
Abstract
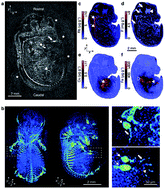
A step-change in the utility of elemental imaging in the biological sciences can be achieved by the integration of quantitative elemental distributions with structural information, allowing novel insights into how tissue development is associated with a dynamic chemical environment. To demonstrate this potential, here we construct a 3D correlative map of biometal distribution and skeletal growth for the first time in a complex organism – in a mouse embryo at developmental stage E14. We achieved this by registering laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) data to micro-computerized tomography (μCT) imagery using endogenous fiducial markers. LA-ICP-MS compositional maps of Rb were used as fiducial markers of dense regions in the micro-CT dataset (e.g. skeletal structure). Results of image registration showed high spatial correlation between both datasets which improved with increasing contrast of the micro-CT images. When coupled with recent advances in analytical instrumentation promoting rapid LA-ICP-MS scanning, this technique promises an enhanced understanding of development in complex biological systems without the need for chemical pre-treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...