Bio-based solvents as entrainers for extractive distillation in aromatic/aliphatic and olefin/paraffin separation†
Abstract
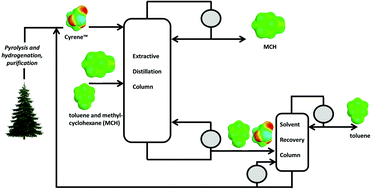
The use of a wide range of bio-based solvents as entrainers in extractive distillation applications was investigated. The separation of hydrocarbon mixtures containing aromatic and aliphatic compounds is highly relevant, and the use of bio-based solvents for this separation was studied using the model system of methylcyclohexane and toluene. Additionally, the use of bio-based solvents for the difficult olefin/paraffin separation was studied using the model system of n-heptane and 1-heptene. From all of the bio-based solvents studied, Cyrene™ showed the highest relative volatility in the methylcyclohexane–toluene system. At compositions up to 40 wt% of methylcyclohexane in the hydrocarbon mixture, with a relative volatility of 3.17 ± 0.16 at 1000 mbar, the selectivity was comparable with the state-of-the-art industrial solvent Sulfolane™. At higher methylcyclohexane fractions, Cyrene™ outperforms Sulfolane™, resulting in a 43% reduction of the minimum reflux ratio, which is an excellent measure of energy efficiency. With regard to the relative volatility of n-heptane over 1-heptene, Cyrene™ also induces an increase in the relative volatility, but not as much as the industrial benchmark n-methylpyrrolidone (NMP). A relative volatility of 1.20 was measured at a solvent-to-feed ratio of 3 (mass basis), which can be further increased by the addition of extra Cyrene™. This leads to the prospect that Cyrene™ may be used for extractive distillation in olefin/paraffin separations, replacing NMP which is subject to severe environmental restrictions by the REACH agreement due to toxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...