Biocatalytic reduction of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids to allylic alcohols†
Abstract
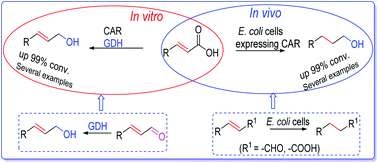
We have developed robust in vivo and in vitro biocatalytic systems that enable reduction of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids to allylic alcohols and their saturated analogues. These compounds are prevalent scaffolds in many industrial chemicals and pharmaceuticals. A substrate profiling study of a carboxylic acid reductase (CAR) investigating unexplored substrate space, such as benzo-fused (hetero)aromatic carboxylic acids and α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids, revealed broad substrate tolerance and provided information on the reactivity patterns of these substrates. E. coli cells expressing a heterologous CAR were employed as a multi-step hydrogenation catalyst to convert a variety of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids to the corresponding saturated primary alcohols, affording up to >99% conversion. This was supported by the broad substrate scope of E. coli endogenous alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), as well as the unexpected C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond reducing activity of E. coli cells. In addition, a broad range of benzofused (hetero)aromatic carboxylic acids were converted to the corresponding primary alcohols by the recombinant E. coli cells. An alternative one-pot in vitro two-enzyme system, consisting of CAR and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH), demonstrates promiscuous carbonyl reductase activity of GDH towards a wide range of unsaturated aldehydes. Hence, coupling CAR with a GDH-driven NADP(H) recycling system provides access to a variety of (hetero)aromatic primary alcohols and allylic alcohols from the parent carboxylates, in up to >99% conversion. To demonstrate the applicability of these systems in preparative synthesis, we performed 100 mg scale biotransformations for the preparation of indole-3-aldehyde and 3-(naphthalen-1-yl)propan-1-ol using the whole-cell system, and cinnamyl alcohol using the in vitro system, affording up to 85% isolated yield.
C bond reducing activity of E. coli cells. In addition, a broad range of benzofused (hetero)aromatic carboxylic acids were converted to the corresponding primary alcohols by the recombinant E. coli cells. An alternative one-pot in vitro two-enzyme system, consisting of CAR and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH), demonstrates promiscuous carbonyl reductase activity of GDH towards a wide range of unsaturated aldehydes. Hence, coupling CAR with a GDH-driven NADP(H) recycling system provides access to a variety of (hetero)aromatic primary alcohols and allylic alcohols from the parent carboxylates, in up to >99% conversion. To demonstrate the applicability of these systems in preparative synthesis, we performed 100 mg scale biotransformations for the preparation of indole-3-aldehyde and 3-(naphthalen-1-yl)propan-1-ol using the whole-cell system, and cinnamyl alcohol using the in vitro system, affording up to 85% isolated yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...