Fast synthesis of hierarchical Al-free Ti-BEA plate-like nanocrystals from low-templated dry gel via a steam-assisted conversion method†
Abstract
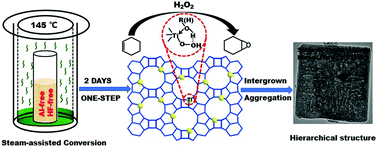
A hierarchical nanosized Ti-BEA zeolite was prepared via a green steam-assisted conversion (SAC) method taking inorganic titanium source as the raw material. Neither aluminum source nor hydrofluoric acid was required, instead, only a bit of template agent (TEAOH/SiO2 = 0.2) and 2 days period were sufficient, much less than that reported (TEAOH/SiO2 ≥ 0.55, 7–14 days). Comprehensively, the role of seeds, alkali ions, and ion exchange on the physicochemical properties of Ti-BEA products were investigated via a series of characterization. Innovatively, the tetracoordinated Ti active sites could be directly constructed by a simple ion exchange process instead of conventional acid washing; furthermore, the mechanism of ion exchange inducing Ti coordination transformation was also proposed to guide other titanosilicate zeolites. Excellent Ti active sites, surface properties, and textural properties endowed the Ti-BEA catalyst with excellent activity over cyclohexene epoxidation, while its synthesis procedure and cost were far better than reported.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...