The direct transformation of bioethanol fermentation residues for production of high-quality resins†
Abstract
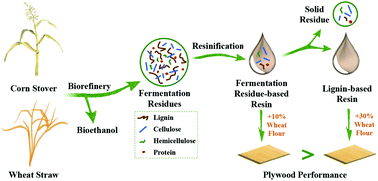
Direct transformation of bioethanol fermentation residues to valuable products is a challenge for current bioethanol fermentation processes. Traditionally, the addition of carbohydrate will reduce the performance of lignin-based resin, which greatly limits the transformation of fermentation residues (lignin-rich component) into resin. In this study, we overcame this challenge by the simple and novel strategy of producing high-quality co-condensed fermentation residue-based resins (FRs) over inexpensive sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate as catalysts. Herein, thorough characterization of the physical properties, chemical structures, and curing behavior was performed to acquire additional data for the prepared resins obtained from two different types of fermentation residues. The current study is the first to meticulously investigate the synergistic effect of lignin and carbohydrates on resins. The mechanism results indicate that numerous co-condensed linkages were formed to produce resins with a firm structure. More importantly, when carbohydrate-rich solid residues were used instead of wheat flour, successful adjustment of viscosity, prevention of excessive osmosis, and increased bonding strength of the FRs occurred. Under the synergistic effect, the produced green FRs were utilized to manufacture plywood with a satisfactory bonding strength (1.07 MPa). The emission of formaldehyde, a harmful volatile organic compound, was also reduced by 94%. This work developed a promising sustainable technology with no waste production for direct transformation of bioethanol fermentation residues from bioethanol manufacturing. The technique reported here vastly broadens the application of fermentation waste and advances the bioethanol industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...