Stachydrine ameliorates the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway: in vitro and in vivo studies†
Abstract
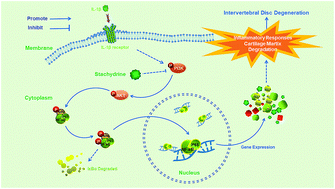
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) has been reported to be a major cause of low back pain. Stachydrine (STA) is present in the fruit juice of the Citrus genus and Leonurus heterophyllus, in non-negligible concentrations. In our study, we examined the protective effects of STA against IDD development as well as its underlying mechanism of action using both in vitro and in vivo experiments. STA exerted protective effects on the anabolism and catabolism of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in IL-1β-treated NPCs and inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory factors in vitro. Mechanistically, STA suppressed the IL-1β-induced activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway cascades. Moreover, it was also demonstrated in molecular docking studies that STA has strong binding abilities to PI3K. Furthermore, STA ameliorated the progression of the IDD process in vivo in the puncture-induced rat model. In summary, our findings demonstrated that STA ameliorates the progression of IDD via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway, which makes STA a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of IDD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...