Walnut protein hydrolysates, rich with peptide fragments of WSREEQEREE and ADIYTEEAGR ameliorate UV-induced photoaging through inhibition of the NF-κB/MMP-1 signaling pathway in female rats
Abstract
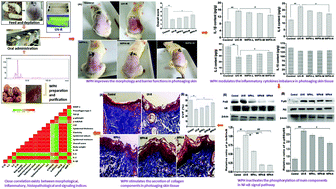
Skin photoaging is a complicated pathological process, and the imbalance of inflammatory regulation is associated highly with photoaging progression. Previously, prepared walnut protein hydrolysates (WPH), rich with peptide fragments of WSREEQEREE and ADIYTEEAGR demonstrated desirable photoprotection. However, it remains unclear if the photoprotection is mediated by the targeted inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Herein, we examined the regulation of WPH on inflammatory cytokine expression, and elucidated the modulation of the NF-κB/MMP-1 signaling pathway by WPH in a photoaging SD rat model. WPH significantly reduced the expression level of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6, but significantly increased the level of IL-2 (all P < 0.05). Furthermore, WPH dramatically inhibited the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway by mitigating the phosphorylation of IκB and p-65 proteins in a dose-dependent manner. The histopathological results indicated that WPH predominately attenuated epidermal hyperplasia, reduced the inflammatory filtration, and promoted collagen deposition in the photoaging skin tissue. Furthermore, WPH significantly stimulated the expression of TGF-β and procollagen type I, and inhibited the MMP-1 activities (all P < 0.05). Overall, the underlying mechanism of WPH ameliorating skin photoaging may be attributed to the synergistic modulation via reversing the inflammatory imbalance, suppressing the activation of the NF-κB signal pathway, stimulating procollagen type I synthesis, and inhibiting MMP-1 activities. According to these results, it can be concluded that WPH has the potential as an anti-photoaging agent in functional foods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...