Effects of probiotic therapy on cardio-metabolic parameters and autonomic modulation in hypertensive women: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial†
Abstract
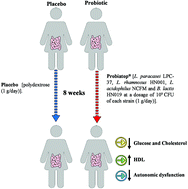
Background and aims: We assessed the effects of probiotic therapy for 8 weeks on cardiometabolic variables and autonomic function in women medically diagnosed with arterial hypertension. Methods and results: Forty women with arterial hypertension, 20–50 years, were assigned to two groups in this randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Patients in the probiotic group received a daily sachet containing Lactobacillus para casei LPC-37, Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001, Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM, and Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 (109 CFU of each strain) for 8 weeks. Patients in the placebo group received identical sachets with polydextrose (1 g day−1, for 8 weeks). Anthropometric, BP, electrocardiogram, biochemical measurements, fecal microbiota composition, and glucose hydrogen breath test were assessed at baseline and after 8 weeks intervention. Anthropometric variables (weight, BMI, and waist circumference) were similar between the two groups (p > 0.05). Probiotic supplementation significantly reduced fasting glucose (change −10.3 mg dL−1, p < 0.05) and cholesterol levels (change −23.6 mg dL−1, p < 0.05), and increased the HDL-cholesterol (change 6.5 mg dL−1, p < 0.05) compared with the baseline condition. Probiotic supplementation lowered, although without statistical significance, systolic BP by about 5 mmHg and diastolic BP by about 2 mmHg in hypertensive women. Lastly, probiotic administration reduced the low frequency (LF) oscillation and LF/high frequency (HF) ratio (p < 0.05) in the frequency domain of heart rate variability, suggesting an improvement in autonomic modulation. Conclusion: Probiotic therapy for 8 weeks reduced fasting glucose levels, and improved the lipid profile and autonomic modulation in hypertensive women.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...