The protective effect of quercetin on retinal inflammation in mice: the involvement of tumor necrosis factor/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
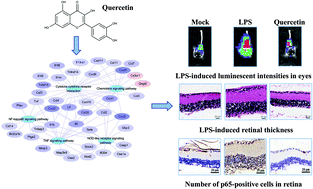
Quercetin is a natural flavonoid that occurs in fruits and vegetables. Retinal inflammation is an important cause of vision loss. This study was aimed to analyze the effects of oral administration of quercetin on retinal inflammation. Transgenic mice, carrying nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-driven luciferase genes, were injected with 1 mg per kg body weight of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Various amounts (1, 10, and 100 mg per kg body weight) of quercetin were orally given to mice. LPS-induced retinal inflammation was evaluated by bioluminescence imaging and histological examination 4 hours later. RNA-Seq analysis of gene expression profiles was performed to explain the mechanisms of quercetin on eye inflammation. Our data showed that LPS enhanced luminescent signals on ocular tissues, while LPS-induced luminescence intensities were significantly suppressed by quercetin by 73.61 ± 21.74%. LPS significantly increased the thickness of retinal tissues by 1.52 ± 0.37 fold, in comparison with the mock, while quercetin reduced the LPS-induced retinal thickness and decreased the accumulation of infiltrating granulocytes. Biological pathway analysis showed that tumor necrosis factor (TNF), cytokine, and NF-κB signaling pathways were involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of quercetin. Immunohistochemical staining further showed that quercetin reduced the activation of NF-κB, the expression of interleukin-1β and TNF-α, and the infiltration of granulocytes in retinal tissues. In conclusion, this is the first study reporting the effects and mechanisms of orally administered quercetin against LPS-induced retinal inflammation in mice. Due to its safety, our study suggested that supplementation of quercetin has beneficial effects on the eyes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...