(−)-Epicatechin protects thoracic aortic perivascular adipose tissue from whitening in high-fat fed mice†
Abstract
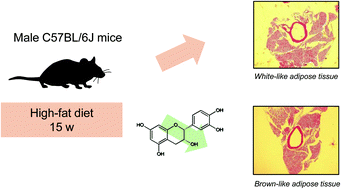
High adipose tissue (AT) accumulation in the body increases the risk for many metabolic and chronic diseases. This work investigated the capacity of the flavonoid (−)-epicatechin to prevent undesirable modifications of AT in mice fed a high-fat diet. Studies were focused on thoracic aorta perivascular AT (taPVAT), which is involved in the control of blood vessel tone, among other functions. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed for 15 weeks a high-fat diet with or without added (−)-epicatechin (20 mg per kg body weight per d). In high-fat diet fed mice, (−)-epicatechin supplementation: (i) prevented the expansion of taPVAT, (ii) attenuated the whitening of taPVAT (according to the adipocyte morphology, diameter, and uncoupling-protein 1 (UCP-1) levels) and (iii) blunted the increase in plasma glucose and cholesterol. The observed taPVAT modifications were not associated with alterations in the aorta wall thickness, aorta tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and NADPH-oxidase 2 (NOX2) expression, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation levels. In summary, our results indicate (−)-epicatechin as a relevant bioactive protecting from the slow and silent development of metabolic and chronic diseases as they are associated with excessive fat intake.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Conference on Polyphenols and Health (ICPH2019) collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...