Amelioration effects of Cirsium japonicum var. maackii extract/fractions on amyloid beta25–35-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells and identification of the main bioactive compound
Abstract
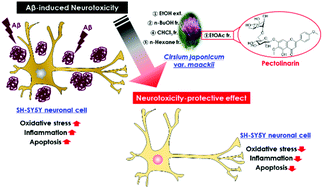
Amyloid beta (Aβ) is a neurotoxic peptide, and the accumulation of Aβ in the brain is the major characteristic of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Recently, the beneficial effects of Cirsium japonicum var. maackii (CJM) on brain health has attracted much attention. In the present study, we investigated the ability and protective mechanisms of CJM to attenuate neuronal toxicity caused by Aβ using SH-SY5Y cells. Aβ25–35 treatment decreased cell viability, whereas CJM extract/fractions increased cell viability in Aβ25–35-treated cells. We found that CJM treatment prevented the accumulation of reactive oxygen species observed in Aβ25–35-treated control cells. Furthermore, Aβ25–35-mediated production of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β was significantly suppressed by CJM. In addition, apoptotic factors were modulated in CJM-treated cells by downregulating B-cell lymphoma-2-associated X protein and upregulating B-cell lymphoma-2 protein expression. The assays showed that the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) fraction of CJM has greater neuroprotective bioactivities compared with the other extract/fractions. The main neuroprotective active compound from the EtOAc fraction of CJM was identified as pectolinarin using ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight-mass spectrometry. Collectively, this study not only describes the neuroprotective effect of CJM against Aβ25–35via the regulation of oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic signaling pathways, but also provides useful information for future studies on the mechanism of novel medicinal sources based on pectolinarin isolated from CJM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...