Analysis of kinetic parameters and mechanisms of nanocrystalline cellulose inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase in simulated digestion of starch†
Abstract
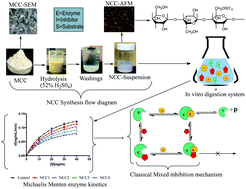
This study evaluated the in vitro inhibitory influence of particle size of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) fractions against α-amylase and α-glucosidase using cooked potato starch–protein food model system. The kinetics of the resulting inhibitions in the presence of NCC of the two tested enzymes were examined and characterised. Both the size and dose of NCC significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited α-amylase and α-glucosidase by modulating the rate of hydrolysis of starch in the food model system lower than that of the control (no added fibre). At equal concentrations of each NCC fraction, the smallest particle size (≤125 nm) exhibited the highest potency as an inhibitor (median inhibitory concentration (IC50) = 2.98 mg mL−1 and 4.57 mg mL−1 for α-amylase and α-glucosidase, respectively). Increasing concentrations of each NCC fraction caused an apparent significant decrease in Vmax values (p < 0.05) with insignificant change in the Km values for both the tested enzymes. Furthermore, binding assays demonstrated that NCC particles may bind to the two tested enzymes in a non-specific manner. Analysis of the kinetics of the enzymes suggested that the mechanism of inhibition showed that the two tested enzymes mainly exhibited non-competitive mode of inhibition. The observed inhibition of the two tested enzymes suggests that reducing the cellulose size ≤125 nm may enhance its inhibition potency and potentially attenuate starch hydrolysis when added to diet.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...