l-Arginine/l-lysine functionalized chitosan–casein core–shell and pH-responsive nanoparticles: fabrication, characterization and bioavailability enhancement of hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive compounds†
Abstract
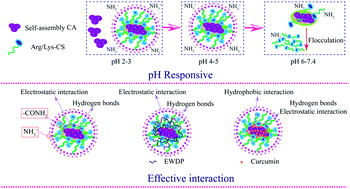
This study aimed at developing novel oral self-assembled delivery systems for the encapsulation, protection, and controlled release of hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive compounds based on L-arginine (Arg)- or L-lysine (Lys)-functionalized chitosan–casein nanoparticles (NPs). The assembled casein (CA) was modified by NaOH and used as a template core for affinity binding with hydrophobic curcumin and hydrophilic egg white-derived peptides (EWDP) and then coated with Arg- or Lys-functionalized chitosan (CS) to stabilize the systems via electrostatic interaction. Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy examination revealed Arg/Lys-CS–CA NPs with the smallest particle size of 110/82 nm, pH-responsive properties, excellent storage stability until 28 days, and spherical shape. The encapsulation efficiency of curcumin and EWDP in the NPs ranged from 81–91%, 35–74% in Arg-CS–CA NPs, and 76–87%, 48–87% in Lys-CS–CA NPs varying with different pH values. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and differential scanning calorimetry analysis were conducted to fully characterize the interaction mechanism of Arg/Lys-CS with CA, as well as the NP incorporation with curcumin and EWDP. The in vitro controlled release profile of the core–shell NPs was obtained up to 24 and 48 h for curcumin and EWDP, respectively. The simulated gastrointestinal digestion experiments confirmed that curcumin and EWDP had higher bioaccessibility in Arg/Lys-CS–CA NPs. This work offers a novel approach for producing core–shell and pH-responsive nanocarriers for oral delivery and bioavailability enhancement of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...