The anti-diabetic effect of eight Lagerstroemia speciosa leaf extracts based on the contents of ellagitannins and ellagic acid derivatives
Abstract
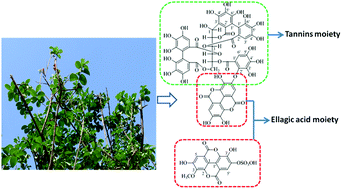
Previously, we have reported the opposite effects of compounds isolated from Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves on a glucose transport (GLUT4) assay. Ellagitannins from L. speciosa activated GLUT4, while ellagic acid derivatives showed an inhibitory effect. As part of our continuing research on anti-diabetic nutritional supplements, we herein compared the anti-diabetic effects of several extracts (LE1–8) from leaves of L. speciosa using different manufacturing processes based on the contents of ellagitannins and ellagic acid derivatives. Their anti-diabetic effects were evaluated through glucose uptake and adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells in vitro as well as alloxan induced diabetic mice in vivo. These extracts were given to mice by gavage at doses of 0.25, 1.0, and 4.0 g per kg body weight once a day for 21 consecutive days. Results showed that LE1 (1.0 g kg−1), LE3 (1.0 or 4.0 g kg−1), LE4 (1.0 or 4.0 g kg−1), LE5 (0.25 or 1.0 or 4.0 g kg−1) and LE7 (1.0 or 4.0 g kg−1) showed significant anti-diabetic effects in alloxan-induced diabetic mice as indicated by the decreased levels of fasting blood glucose, body weight, serum biomarkers, tissue weight and body fat, and increased final insulin levels. LE8 (1.0 g kg−1) showed a moderate anti-diabetic effect as illustrated by the reduced fasting blood glucose level while LE2 and LE6 showed slight effects in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. The potential correlation of the content of ellagitannins, ellagic acid derivatives, and corosolic acid with the anti-diabetic activity was discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...