Vinegar extract ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damage associated with the modulation of gut microbiota in mice†
Abstract
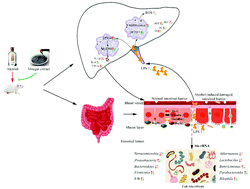
Vinegar extract is rich in phenolic compounds, which can prevent free radical-induced diseases. The aim of the present study was to explore the effects of vinegar extract on gut microbiota in alcohol-treated mice and their correlation with alcohol-induced liver damage. These results showed that vinegar extract regulated the gut microbiota composition and improved intestinal homeostasis through increasing the expression levels of ZO-1, occludin, claudin-1, Reg3b, and Reg3g in alcohol-treated mice. In addition, vinegar extract inhibited the alcohol-induced production of ROS and inflammatory factors. Moreover, Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, Akkermansia, and Lactobacillus showed a significant positive correlation with Reg3b, Reg3g, ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 and a negative correlation with hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress parameters. However, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Butyricimonas, Parabacteroides, and Bilophila exhibited the opposite effect. These findings suggest that vinegar extract modulates gut microbiota and improves intestinal homeostasis, and can be used as a novel gut microbiota manipulator against alcohol-induced liver damage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...