Ethanolamides of essential α-linolenic and linoleic fatty acids suppress short-term food intake in rats
Abstract
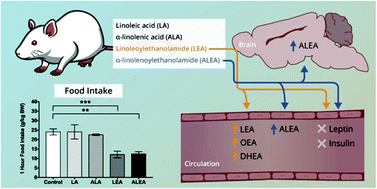
Food source has a significant impact on levels of fatty acids and their derivatives, fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs), in the small intestine and brain. Among non-essential fatty acids, oleic acid and its FAE acutely reduce food intake. However, effects of the essential α-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, and their FAEs on appetite regulation remain undefined. This study tested the hypothesis that α-linolenic acid and linoleic acid mediate acute suppression of food intake through their corresponding FAEs, α-linolenoylethanolamide and linoleoylethanolamide, respectively. To allow for the differentiation of the effects of FAEs and their parent fatty acids, male Wistar rats were injected intraperitoneally with α-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, α-linolenoylethanolamide and linoleoylethanolamide after a 12-hour overnight fast. Short-term food intake, plasma and brain FAE status, and plasma concentrations of insulin and leptin were measured to determine whether these hormones mediate the anorectic effect of FAEs. Both ethanolamides, but not their parent fatty acids, acutely suppressed food intake up to one hour post-treatment and this effect was independent of insulin and leptin hormones. In conclusion, essential α-linolenic and linoleic fatty acids mediate acute suppression of food intake through their corresponding FAEs. These findings may aid in the further research of FAEs as potential therapeutic agents for the management and treatment of obesity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...