Nutritional and sensory characteristics of bread enriched with roasted prickly pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) seed flour
Abstract
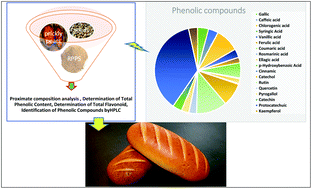
The present study aims to investigate the nutritional, antioxidative, and sensory characteristics of bread enriched with roasted prickly pear seed (RPPS) flour. Six flour blends were formulated by partial replacement of wheat flour with 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10% RPPS flour. Proximate composition, phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant activity measured using a 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical of wheat and RPPS flours were determined. Nutritional and sensory characteristics of bread enriched with different levels of RPPS flour were evaluated. The results show that the content of total phenolics, flavonoids and radical scavenging activity in RPPS flour were about 4.5, 4.7 and 4.0 fold higher, respectively, when compared to wheat flour. The incorporation of different levels of RPPS flour in bread formulation significantly increases the dietary fibers, fat, and ash contents and reduces the carbohydrate content of the produced breads. The highest (p ≤ 0.05) phenolic concentrations and antioxidant activity values were found in bread enriched with 6, 8 and 10% RPPS flour. Generally, the replacement of wheat flour with RPPS flour results in a significant decrease (p ≤ 0.05) in the specific volume, however, no significant difference (p ≥ 0.05) was observed between the 2% RPPS-enriched flour and control breads. The sensory properties of breads were not affected at low levels up to 6% supplementation, but at more than 6% RPPS flour supplementation, the bread became unacceptable.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...