A standardised semi-dynamic in vitro digestion method suitable for food – an international consensus†
Abstract
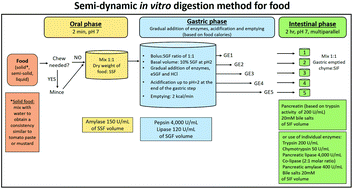
The link between food and human health is increasingly a topic of interest. One avenue of study has been to assess food disintegration and interactions within the gastrointestinal tract. In vitro digestion models have been widely used to overcome the constrictions associated with in vivo methodology. The COST Action INFOGEST developed an international, harmonised protocol for static simulation of digestion in the upper gastrointestinal tract of adults. This protocol is widely used; however, it is restricted to providing end-point assessment without considering the possible structural changes. On the other hand, there are dynamic models that provide more physiologically relevant data but are expensive and difficult to access. There is a gap between these models. The method outlined in this article provides an intermediate model; it builds upon the harmonised static model and now includes crucial kinetic aspects associated with the gastric phase of digestion, including gradual acidification, fluid and enzyme secretion and emptying. This paper provides guidance and standardised recommendations of a physiologically relevant semi-dynamic in vitro simulation of upper gastrointestinal tract digestion, with particular focus on the gastric phase. Adaptations of this model have already been used to provide kinetic data on nutrient digestion and structural changes during the gastric phase that impact on nutrient absorption. Moreover, it provides a simple tool that can be used in a wide range of laboratories.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent Open Access Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...